Arthroscopy (arthroscopy surgery, arthroscopy, arthroscopic surgery) is a minimally invasive surgical procedure performed for the diagnosis and/or treatment of injuries to the inner part of the joint. It is performed using an arthroscope – a type of endoscope that is inserted into the joint through a micro-incision.
Arthroscopic manipulations can be performed to diagnose and treat many orthopedic conditions, including articular mice, rupture of the cartilage surface, rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament, and removal of damaged cartilage.
The advantage of arthroscopy over traditional open surgery is that the joint does not open completely. Instead, for example, in arthroscopy of the knee, only two small holes are made – one for the insertion of the arthroscope, the other for surgical instruments, with which a complete removal of the patella can be performed. This shortens the postoperative recovery process and increases the success rate of the operation since the degree of damage to the connective tissues is much lower than in the case of open surgery. This is especially useful for professional athletes who often experience knee injuries and need to recover quickly. Also, after arthroscopy, the scars remain less noticeable due to the small size of the incisions.
In arthroscopy, surgeons inject irrigation fluid into the articular cavity, which is used to separate the joints and organize the space for the operation. Surgical instruments used in arthroscopy are smaller than traditional ones. Doctors, observing the area of the joint on a video monitor, can diagnose and operate tears of the joint tissues: ligaments, menisci, and cartilage.
It is technically possible to make arthroscopic diagnostics of almost any joint in the human body. Arthroscopy of the following joints is most commonly performed:
- Knee-joint
- Shoulder joint
- Elbow joint
- Hip joint
- Ankle joint
In the DMC clinic, arthroscopic interventions are carried out on the German Tekna arthroscope, which is a leader in the quality of optical products in the world, by highly qualified specialists trained in leading clinics in South Korea, Germany, England and having practical experience in reconstructive and restorative surgeries on large joints.
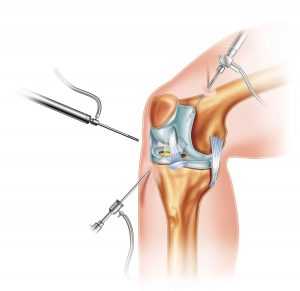
Indications for Arthroscopy
- Damage to the menisci;
- Injuries to the cruciate ligaments of the knee joint;
- Inflammatory diseases of the synovial membrane;
- Habitual dislocation of the patella;
- Articular cartilage damage and disease;
- Damage and disease of the fatty body – chronic hyperplasia of the fatty body (Goff’s disease);
- Deforming arthrosis of the knee joint;
- Unclear clinic for joint damage or disease, which cannot be sufficiently clarified using clinical and radiological research methods;
- Unclear complaints after previously performed surgical interventions.
What arthroscopic operations we perform in our Center:
- Arthroscopic removal of meniscus;
- Meniscus suture;
- Arthroscopic plasty of the anterior and posterior cruciate ligament;
- Removal of chondromic bodies;
- Resection of synovial folds and fatty body of the knee joint;
- Rehabilitation arthroscopy of the knee joint for deforming arthrosis;
- Diagnostic arthroscopy of the knee joint;
- Arthroscopic stabilization of the shoulder joint in case of habitual shoulder dislocation.
Arthroscopic meniscus removal, meniscus suture
The aim of the operation is to preserve the body of the meniscus as much as possible. The decision as to whether or not to attempt repair of a tear is based on several factors, including the age of the injury, the age of the patient, knee stability, the location of the tear, and its orientation. A tear with a high chance of successful healing is a fresh longitudinal tear in the peripheral third of the meniscus in a young patient. Degenerative processes, displaced tears, horizontal dissections, and complex lesions are poor candidates for healing. Young patients are more likely to be successful. Displaced tears may require removal of the part of the meniscus that has come off (meniscectomy).
Meniscus surgery in modern clinics is done by arthroscopy, which is performed through several small surgical openings and takes approximately 1 hour. The surgeon through these holes inserts surgical instruments into the joint cavity, including a small video camera that allows you to see the joint from the inside.
The terms of rehabilitation are determined by the doctor individually. Patients who have partially or completely removed their meniscus should prepare to walk on crutches for 4 to 7 days. A small swelling may persist for 3-6 weeks. After 4-6 weeks, and maybe even earlier, the patient will be able to return to normal physical activity. If the meniscus tear has been sutured, the crutches should be used much longer (4-6 weeks) and the injured knee should not be stressed to allow the meniscus to heal completely. Compared to legacy open knee surgery and large surgical incisions, arthroscopic surgery minimizes the necessary tissue damage, which of course greatly shortens the recovery time after surgery and allows you to quickly return to work and sports.
Arthroscopic plasty of the anterior and posterior cruciate ligament
The ligament is restored arthroscopically from the patient’s or donor’s tissue using fixation implants.
Arthroscopic stabilization of the shoulder joint for habitual shoulder dislocation
Arthroscopic surgery is a treatment option for this pathology, the main advantage of which is its low trauma (the joint capsule is damaged in small (7-9 mm) areas required for carrying out special instruments.
The essence of arthroscopic operations is to eliminate (suture) that defect of the capsule and the articular lip of the scapula (namely, the pathology of these structures led to the dislocation of the humeral head, which means we eliminate the very cause of the dislocation, in contrast, to open stabilizing operations, where the purpose of the operation is to create from structures surrounding the joint of some obstacle in the path of dislocation).
With the correct execution of this operation, success is achieved in 95% of cases.
However, arthroscopic surgery for shoulder instability is not recommended for everyone. With certain pathological changes in the articular surface of the scapula and joint capsule, changes in the head of the humerus, with the formation of significant defects, it becomes necessary to open surgical interventions, which are also carried out in our Center.





