The prosthesis is an artificial device that can replace the function of a specific organ. If the prosthesis is located inside the human body, then it is called an endoprosthesis.
Endoprosthetics of joints is an operation to replace joint components with implants that have the anatomical shape of a healthy joint and allow you to perform the entire range of motion.
After such operations, the patient forgets about pain in the joints and returns to an active life. The center performs endoprosthetics of large (knee, hip, shoulder, elbow) and small (finger) joints.
The materials from which modern joint endoprostheses are made have high strength and good survival rate in the human body. Therefore, their service life is on average 15-20 years, and in many cases, patients use them for up to 30 years. When the endoprosthesis is worn out, it is replaced with a new one.
Metal endoprostheses are made from various stainless steel alloys. They are fixed to the bone using special cement, which is acrylic resin and alloys of cobalt and chromium. For the manufacture of sliding components of endoprostheses, for example, the head of the humorous or femur, titanium alloys are used. And for the manufacture of sliding surfaces, heavy-duty polyethylene and alumina ceramics are used.
For the manufacture of prostheses, ceramics, metals, and especially durable plastics are used. These materials must have good wear resistance and be easy to process to achieve a good fit between the components of the prosthesis. The production of prostheses is a complex technological process. Each prosthesis undergoes multi-stage control and is certified.
Endoprosthetics surgery is used for various diseases and injuries of the articular apparatus, which have led to a complete or almost complete loss of motor functions. Such joint diseases include:
- Degenerative-dystrophic diseases (all types of osteoarthritis and arthritis)
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Aseptic necrosis of the femoral head
- Intra-articular fractures
- False joints
- Joint dysplasia
- Hip fracture
Absolute contraindications for surgery:
– diseases of the cardiovascular, bronchial-pulmonary system in the stage of decompensation;
– presence of a focus of purulent infection (tonsillitis, carious teeth, chronic sinusitis, and otitis media, pustular skin diseases);
– mental or neuromuscular disorders;
– active or latent infection in the joint area less than 3 months old;
– immaturity of the skeleton;
– impossibility of movement;
– polyallergy;
– the absence of the medullary canal of the femur.
– acute vascular diseases of the lower extremities (thrombophlebitis, thromboembolism).
Relative contraindications:
– oncological diseases;
– chronic somatic diseases,
– liver failure,
– hormonal osteopathy,
– obesity of the 3rd degree.
Endoprosthetics surgery can be complete (total) or incomplete (partial). With partial endoprosthetics, only worn parts of the joint are replaced, for example, the head of the bone or the glenoid cavity. Therefore, such an operation is also called unipolar arthroplasty. Unlike unipolar prosthetics, with total prosthetics, the entire joint is replaced with an endoprosthesis.
Before the operation, the patient undergoes a thorough examination, during which indications and contraindications for surgical intervention are determined, as well as a careful selection of the necessary prosthesis, is performed. Most often, arthroplasty operations take place without serious complications and allow in almost all cases to achieve restoration of the patient’s motor activity, as well as relieve him of years of pain.
Hip arthroplasty is a surgical procedure aimed at restoring a movable painless joint, allowing you to return to your normal life.
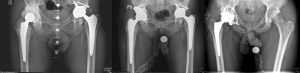
Endoprosthetics of the hip joints is carried out at the Center with modern implants from the world’s leading manufacturers:
– primary – total,
– primary – superficial,
– revision (repeated).
Modern hip joint endoprostheses are complex technical products. Just like a normal hip joint, an artificial hip joint consists of a round head and a concave cavity in which the head rotates, allowing for normal range of motion. Typically, prosthesis consists of a stem, head, cup and insert.
The appropriate prosthesis is selected for each specific case. Each of the components has its own size range.
Hip joint prostheses are distinguished by the type of fixation:
- cement-retained endoprostheses;
- endoprostheses without cement fixation.
The Center uses modern hip joint endoprostheses that have proven themselves in international practice.

Surgery to replace a hip joint with a prosthesis is a complex high-tech procedure. Therefore, the preoperative examination of the patient is of great importance, the selection of the type of endoprosthesis adequate for each specific case, as well as strict adherence to the recommendations after the operation.
Consultation. During the consultation, the doctor will determine the indications and contraindications for arthroplasty, conduct the necessary research and select the appropriate prosthesis. X-ray examination will allow to find out the degree of deterioration of the joint, to make the necessary measurements. You will be sure to be warned about the possible risks and complications of the operation. The complications of the operation include the following:
- infection in the area of the operation;
- blood loss during or after surgery;
- thromboembolism (blockage of a vessel by a thrombus);
- the development of pneumonia;
- dislocation of the prosthesis, which will require an increase in the duration of treatment.
Before the operation. Before the operation, the patient undergoes a complete clinical examination (delivery of tests, specialist consultations, examination by an anesthesiologist). Hospitalization of the patient 1-2 days before the operation.
Operation. In standard cases, implantation of an artificial joint lasts 1-2 hours.
During the operation, the hip joint destroyed by the disease is irretrievably removed from the body. After that, an endoprosthesis is installed in its place. The surgeon removes the head and neck of the femur, and in their place, the parts of the endoprosthesis (head and femoral stem) are fixed. The acetabulum is drilled out, and an artificial cavity is inserted in its place, which is fixed with screws or cement. After checking the function of the limb, the surgical wound is sutured in layers. To remove blood that may accumulate in the wound after surgery, a silicone drainage tube is installed on the lateral surface of the thigh.
During the operation, measures are taken to prevent infectious complications, if necessary, replenishment of blood loss, and drainage of the wound in order to prevent blood accumulation.
After operation. In the postoperative period, the administration of antibiotics, painkillers, symptomatic treatment continues. A roller is placed between the legs to hold the operated limb in the correct position. Activation in bed is allowed already on the 1st day after the operation. From the second day, you can sit down in bed, start static exercises for the muscles of the limb, and perform breathing exercises. Walking with a dosed load on the operated limb and additional support (crutches, playpen) is possible as early as 3 days. The stitches are removed for 10-12 days.
In-patient discharge. Discharge is made 10-12 days after the operation. Rehabilitation measures should be continued, strictly following the recommendations of the operating surgeon. If necessary, hospitalization for recovery is possible under the guidance of rehabilitologists. Restrictions in physical activity on the operated limb should be observed within 6-8 weeks from the operation, during which time it is recommended to use additional support.
Knee arthroplasty is a very precise surgical intervention, the purpose of which is to return you to a movable painless joint, allowing you to return to your usual life. Knee arthroplasty is necessary when the destruction of the knees is so great that a joint-preserving intervention is no longer worthwhile.
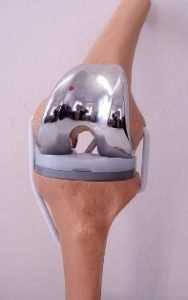
The center performs primary (total) and repeated (revision) knee arthroplasty.
Just like a regular knee joint, an artificial one exactly repeats the elements of a normal joint, allowing the required range of motion. The appropriate prosthesis is selected for each specific case. Endoprosthetics of knee joints is carried out at the Center with modern implants from leading world manufacturers.
Consultation. During the consultation, the doctor will determine the indications and contraindications for arthroplasty, conduct the necessary research and select the appropriate prosthesis. X-ray examination will allow to find out the degree of deterioration of the joint, to make the necessary measurements. You will be sure to be warned about the possible risks and complications of the operation. The complications of the operation include the following:
• infection in the area of the operation
• blood loss during or after surgery
• thromboembolism (blockage of a vessel by a thrombus)
Before the operation. Before the operation, the patient undergoes a complete clinical examination (delivery of tests, specialist consultations, examination by an anesthesiologist). Hospitalization of the patient 1-2 days before the operation.
Operation. In standard cases, implantation of an artificial joint lasts 2 hours. During the operation, after opening the capsule of the knee joint and exposing the articular surfaces of the bones, partial removal of bone tissue is performed. The posterior surface of the patella (patella) is also removed. In this case, the ligamentous structures of the joint (lateral and cruciate ligaments) remain unaffected. To improve the function of the knee joint, the surgeon may restore the integrity of the ligaments that strengthen the knee joint.
Further, artificial pads are installed on the prepared surfaces of the bones that form the knee joint. The shape of the endoprosthesis pads follows the shape of the articular surfaces of the knee joint, so the range of motion in the prosthetic joint is about the same as in a normally functioning knee joint. At the end of the operation, before suturing, drainage is installed in the wound, through which the outflow of wound contents (blood, exudate) will occur. During the operation, measures are taken to prevent infectious complications, if necessary, replenishment of blood loss, drainage of the wound in order to prevent blood accumulation.
After the operation, the patient is transferred to the department of anesthesiology and intensive care.
After operation. In the postoperative period, the administration of antibiotics, painkillers, symptomatic treatment continues. Activation in bed is allowed already on the 1st day after the operation. From the second day, you can sit down in bed, start static exercises for the muscles of the limb, and perform breathing exercises. Walking with a dosed load on the operated limb and additional support (crutches, playpen) is possible already from 3 days. Exercise is very important and reduces the risk of complications such as thrombosis, etc. later followed by intensive therapeutic exercises, which help to strengthen the muscles and improve mobility. The stitches are removed for 10-12 days.
Discharge home. Discharge is made 10-12 days after the operation. Rehabilitation measures should be continued, strictly following the recommendations of the operating surgeon. If necessary, hospitalization for recovery is possible under the guidance of rehabilitologists. Restrictions in physical activity on the operated limb should be observed within 6 weeks from the operation, during which time it is recommended to use additional support. From 4-5 weeks walking with support on a cane.
The intensity of physical activity associated with severe concussions (eg jolting, jumping), in which the prosthesis is subjected to shocks and/or increased stress (eg heavy physical activity, marathons, etc.) can reduce the success of the surgery and the duration of the implant’s life. Even if no pain occurs, the artificial joint should be examined regularly by a doctor.
Shoulder arthroplasty is an effective and often the only way to restore lost limb function. As a result of this operation, all functions of the shoulder joint are restored and pain in the shoulder disappears.
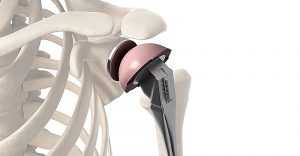
The appropriate prosthesis is selected for each specific case. Depending on which part of the joint is replaced, shoulder joint endoprostheses are total and unipolar.
Unipolar prostheses are implants that replace only one element of the joint, usually the head of the humerus.
Total shoulder arthroplasty implies the replacement of all elements of the joint, i.e. the head of the humerus, and the glenoid cavity of the scapula. The design of the prosthesis consists of a head, a neck, and a segment of the diaphysis of various types and sizes. Shaft prostheses are available for cemented or cementless anchorage.
Consultation. During the consultation, the doctor will determine the indications and contraindications for arthroplasty, conduct the necessary research and select the appropriate prosthesis. X-ray examination will allow to find out the degree of deterioration of the joint, to make the necessary measurements. You will be sure to be warned about the possible risks and complications of the operation. The complications of the operation include the following:
• infection in the area of the operation;
• blood loss during or after surgery;
• thromboembolism (blockage of a vessel by a thrombus);
• dislocation of the prosthesis, which will require an increase in the treatment time.
Before the operation. Before the operation, the patient undergoes a complete clinical examination (delivery of tests, specialist consultations, examination by an anesthesiologist). Hospitalization of the patient 1-2 days before the operation.
Operation. In standard cases, implantation of an artificial joint lasts 2 hours. During the operation, measures are taken to prevent infectious complications, if necessary, replenishment of blood loss, drainage of the wound in order to prevent blood accumulation.
After operation. In the postoperative period, the administration of antibiotics, painkillers, symptomatic treatment continues. The upper limb is fixed on a kerchief bandage.
Rehabilitation in a hospital. Activation on the 1st day after surgery. From the second day, you can start static exercises for the muscles of the arms. During the first week after the operation, the hand into which the prosthesis was implanted can only be performed passive movements (not voluntary, but with the help of a physical therapy therapist or a healthy hand).
Then the patient is allowed active movements, but with the support of a healthy hand. From 15-18 days after the operation, you can begin to perform active movements with a small load. The use of a special set of exercises allows you to achieve a significant amount of movement at discharge. Physiotherapy is underway. The stitches are removed for 10-12 days.
Discharge home. Discharge is made 10-12 days after the operation. Rehabilitation measures should be continued, strictly following the recommendations of the operating surgeon. If necessary, hospitalization for recovery is possible under the guidance of rehabilitologists. For the first 3 weeks after surgery, it is recommended to wear a kerchief or shoulder brace. Restrictions in physical activity on the operated limb should be observed within 4-6 weeks from the operation. Swimming pool sessions are scheduled 8 weeks after surgery. Physical education and sports, without restrictions, are allowed 3 months after the operation.





