Operations on the bones and joints of the foot are performed for traumatic injuries, congenital (for example, clubfoot) and acquired (Hallus valgus, hammertoes) deformities, and some chronic diseases. Sometimes interventions are carried out to eliminate the long-term consequences of injuries, to improve the support function of the limb in case of paresis and paralysis. As a method of pain relief, conductive anesthesia is usually used; in some cases, operations on bones and joints are performed under general anesthesia or local anesthesia. Access and scope of intervention depend on the nature and extent of the pathological process.
Treatment of forefoot deformities has a long and rich history and is extremely varied. Currently, depending on the degree of development of the disease, both conservative and surgical methods of treatment are used. At the initial stages of flat feet, the orthopedic surgeon prescribes a set of measures, including therapeutic exercises, in order to restore the natural state of the shape of the foot, and also recommend orthopedic shoes, individual insoles that form or correct the arches of the foot. Among the operational techniques, more than 300 types of operations are known, most of which are only of historical interest.
Among the many operations on the forefoot, osteotomies at various levels of the metatarsal bones and phalanges are quite popular. Due to its effectiveness and the lack of the need for plaster immobilization, and, consequently, shortening the postoperative recovery period, osteotomies of the first metatarsal bone of the SCARF, Shevron type are popular among patients and orthopedic traumatologists.
In the “DMC” center, on the basis of modern achievements of local and foreign orthopedics, the whole range of conservative and surgical treatment of patients with static deformities of the forefoot is performed.
Unique modern surgical techniques for treating deformities of the forefoot, including various types of osteotomies of the metatarsal bones and phalanges of the toes with hallux valgus, hammer-like deformities of the toes. The surgical methods of treatment used in the center exclude the use of immobilizing devices, plaster casts in the postoperative period, and do not require the use of crutches. The hospital stay can be from 3 to 5 days.
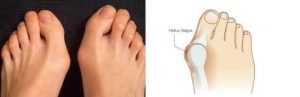
Hallux valgus surgery is a surgical intervention to eliminate deformity in the area of the first metatarsophalangeal joint. The indication for surgery is a cosmetic defect, pain syndrome, and progression of deformity, corns, and other pathological manifestations of Hallux valgus. There are a large number of techniques for correcting this deformity; the method of intervention is selected individually, taking into account the severity of the pathology and other factors.
Types of surgery
There are many different techniques for eliminating deformity in Hallux valgus. The choice of the technique is carried out by the orthopedist, taking into account the severity of the pathology, the patient’s age, concomitant changes in the adjacent parts of the foot. The main types of surgical interventions used in modern orthopedics include:
A simple removal of a protruding bone fragment (Shede type surgery). The intervention is called exostectomy and is indicated for mild deformity.
Hallux valgus operation during which the ligaments surrounding the first metatarsophalangeal joint are restored.
Resection arthroplasty. It consists of the excision of the head of the first metatarsal bone.
Arthrodesis. The articular surfaces are excised; the joint is fixed and becomes motionless.
Arthroplasty. The joint surfaces are replaced with synthetic implants.
It is also possible to correct the deformity by osteotomy. The essence of the intervention is to remove a fragment of one or more bones. Most often, a small section of the first metatarsal bone is removed, less often a fragment of the main phalanx of the first finger. Sometimes a technique is used that involves the removal of sections of both bones; in some cases, a fragment of the sphenoid bone is excised (the bones of the tarsus, with which the first metatarsal bone is connected). Partial bone removal is performed to correct angular displacement. After excision of the bone fragment, the fragments are fixed in the anatomically correct position.
Methodology
Surgical intervention is performed in a planned manner. Before a hospitalization, the patient is examined, general tests are prescribed, and radiographs of the first metatarsophalangeal joint are performed. As a method of anesthesia, conduction anesthesia and general anesthesia are used. The incision is made along the dorsum of the foot over the affected area. To remove bone structures, use a chisel, an oscillatory saw. After carrying out the planned surgical measures, the wound is sutured, a rubber graduate is installed.
After surgery for Hallux valgus, the limb is fixed with comfortable orthopedic shoes. The duration of immobilization varies depending on the type of surgery performed. The discharge time is determined by the presence of edema, the condition of the postoperative wound, and the general condition of the patient. The stitches are removed for 10-12 days. Subsequently, it is recommended to choose comfortable shoes, refuse to wear high-heeled shoes, and perform special exercises.





