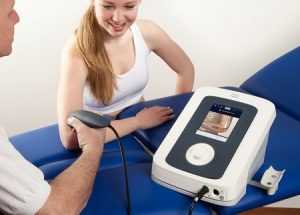
Ultrasound therapy using a “Sonoplus 490” (Holland) ultrasound apparatus
The Sonopuls ultrasound therapy device uses high-frequency mechanical vibrations (1 or 3 MHz, depending on the operating mode of the ultrasound emitter). Oscillations, getting into the patient’s body, have a mechanical, thermal, and biological effect.
Sonopuls ultrasound therapy devices (models 190, 490, 692id) have proven themselves well in the treatment of muscular and ligamentous apparatus, anti-inflammatory, and analgesic therapy. Exposure to ultrasonic vibrations has an effective anti-inflammatory, absorbent, analgesic effect and is used in most physiotherapy departments in Europe.
Until recently, all ultrasound procedures were performed by medical staff using a “scanning technique” to avoid hot spots in the tissues. New devices with the function of ultrasound therapy Sonopuls 490 allow using the StatUS static ultrasound technique, which has many significant advantages over classical ultrasound therapy.
Firstly, the permanently installed ultrasonic emitter of the Sonopuls apparatus affects the treatment area during the entire procedure, while the scanning technique only affects 50-60% of the duration of the procedure.
Secondly, the time of the medical staff is saved – there is no need to be near the patient during the entire procedure.
Thirdly, instead of the classic UST gel, special gel pads are used that do not pollute the skin and clothes of patients, as well as the emitter itself.
Fourthly, the StatUS emitter of Sonopuls ultrasound devices has a vacuum overlay, which provides a very fast and reliable fixation on the patient, regardless of the area of placement.
The latest models of the Sonopuls 490 ultrasound therapy device also support the static superposition mode of the ultrasound emitter.
The indications for the use of ultrasound therapy devices are:
- diseases of the musculoskeletal system: injuries to muscles, tendons, and joints;
- neurological manifestations of spinal osteochondrosis (with the radicular-vascular syndrome, myelopathy);
- injuries and diseases of the peripheral nervous system, neuropathy, neuralgia, sciatica, spinal and spinal cord injuries, multiple sclerosis, Raynaud’s disease;
- inflammatory processes and edematous conditions in dentistry;
- mastitis;
- diseases of the ENT organs;
- surgical pathology (keloid scars, adhesive disease, infiltrates).